Q1: What role does material selection play in industrial filtration fabrics?
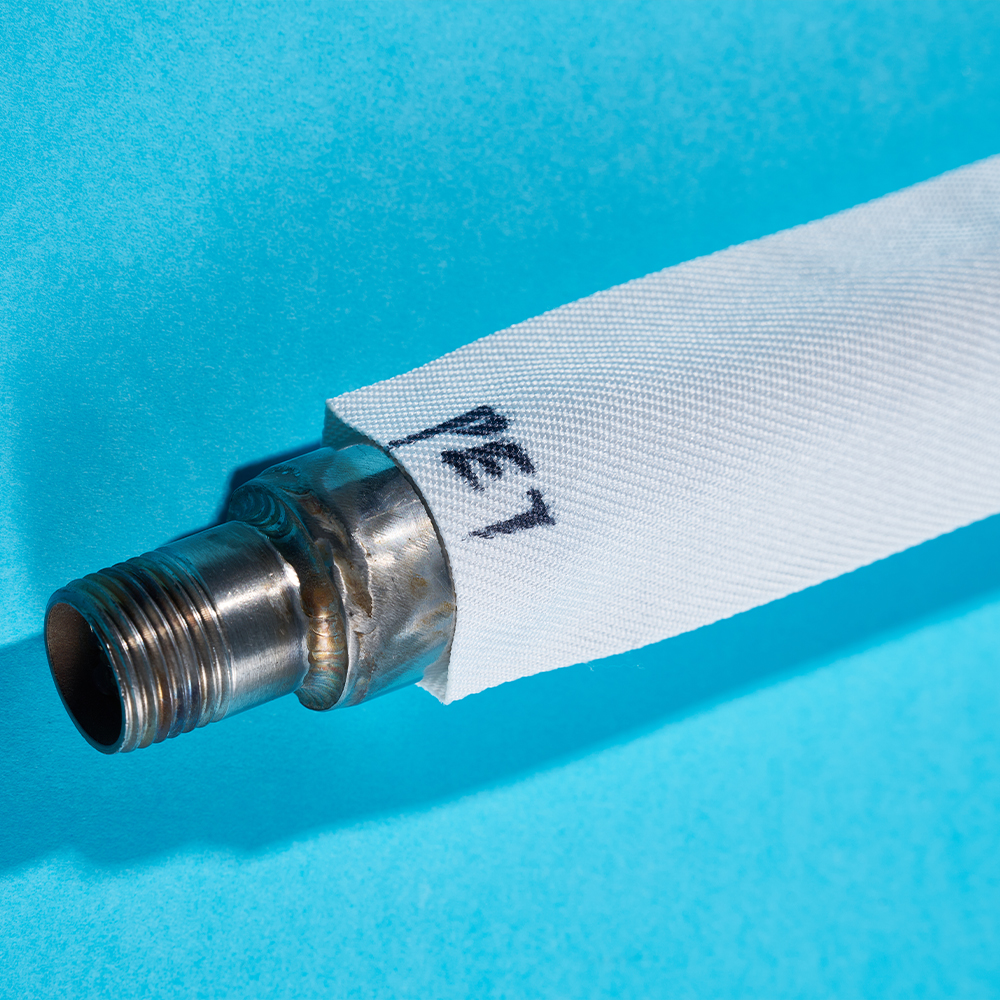
In the filtration fabric manufacturing industry, material selection determines how a product performs under real operating conditions. An Industrial Filtration Fabric is often exposed to continuous airflow, liquid pressure, or chemical contact. Manufacturers therefore evaluate fiber strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability before production begins.
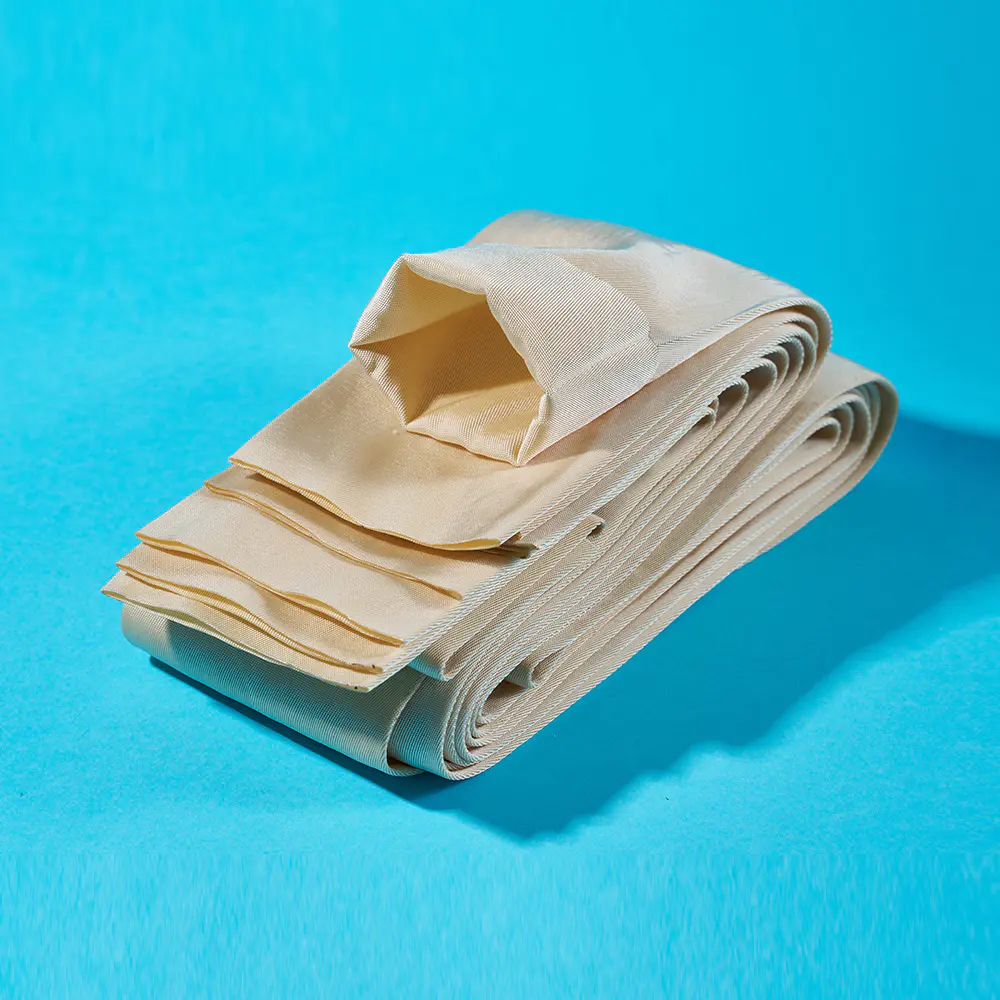
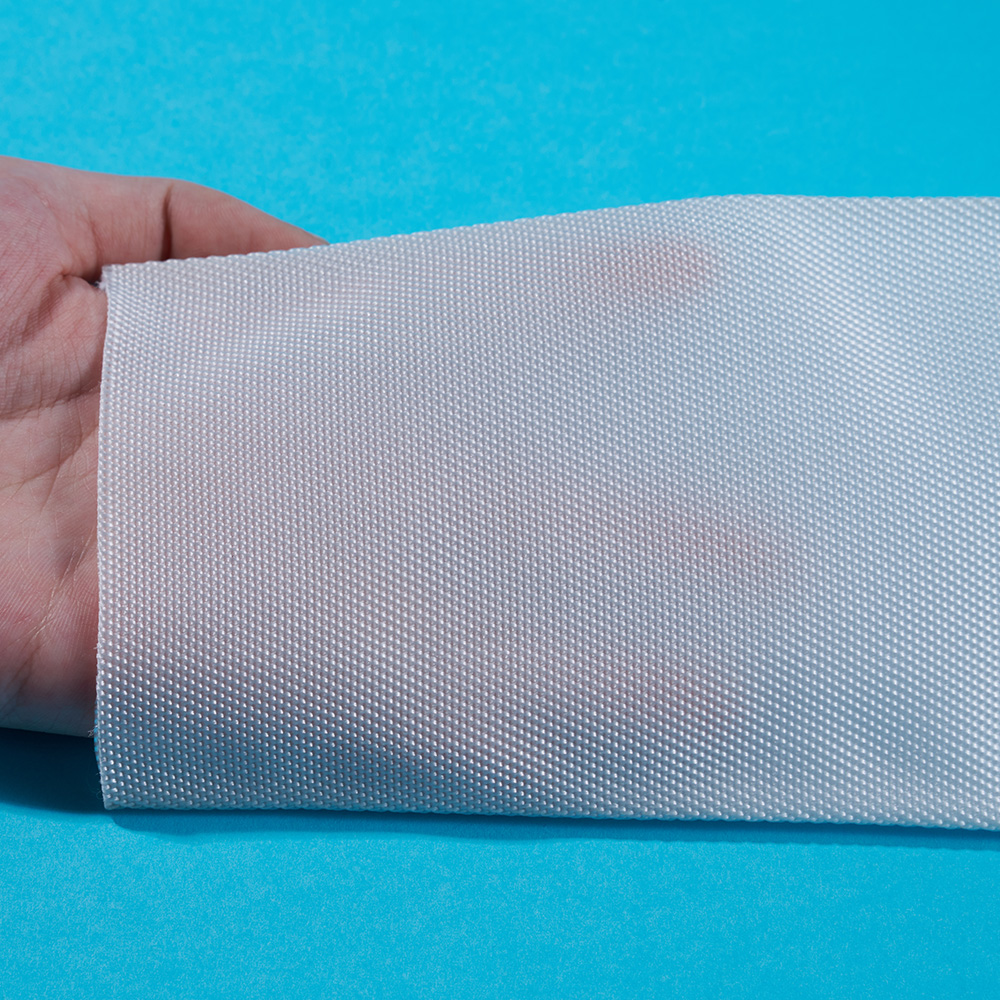
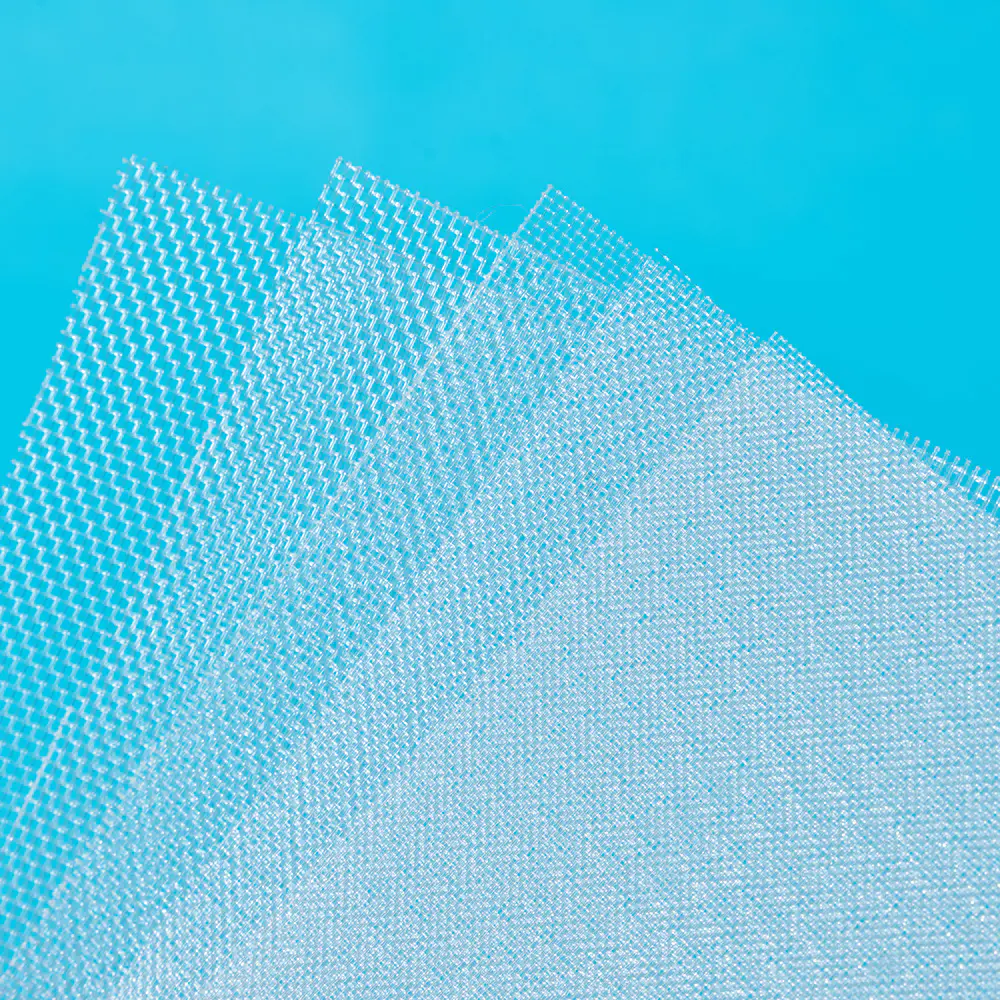
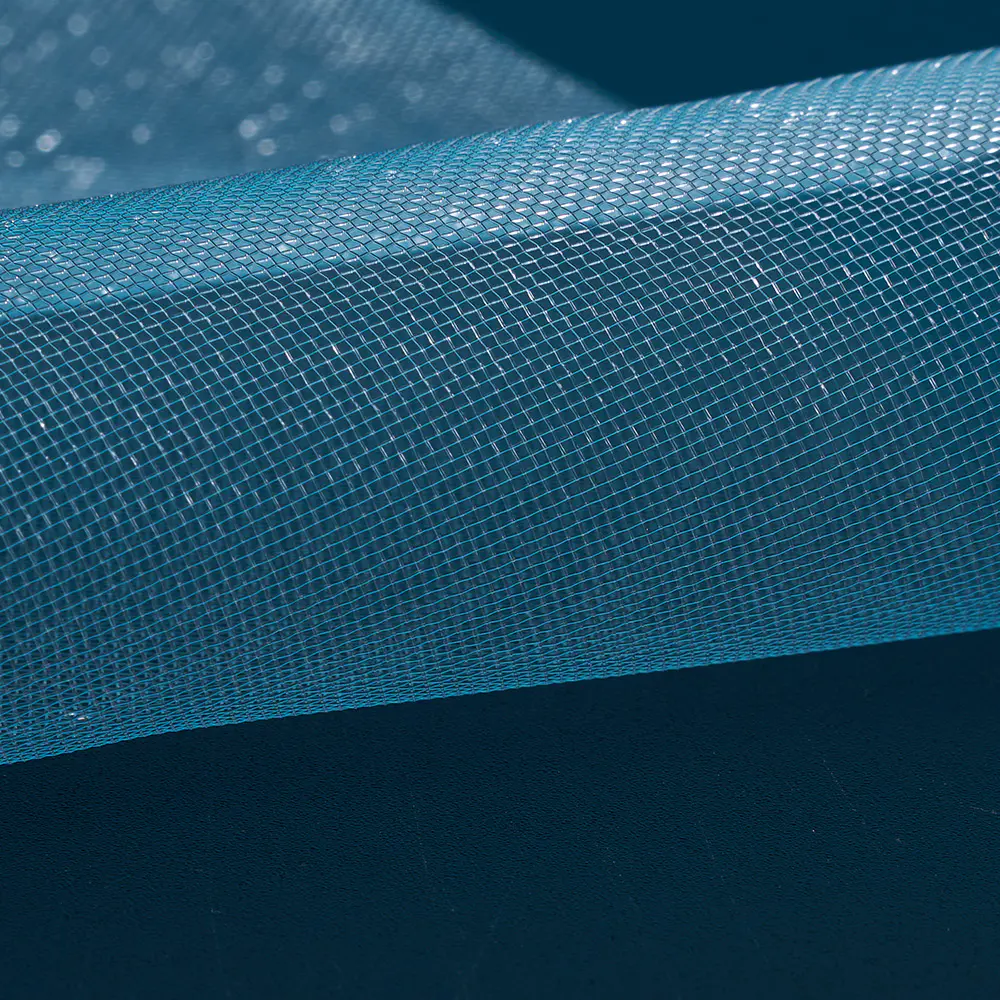
A Multifilament Filter Textile is frequently chosen when higher tensile strength and dimensional stability are required. Because this type of textile is constructed from multiple fine filaments twisted together, it offers improved durability compared to single-filament structures. From a manufacturing standpoint, controlling filament uniformity during spinning helps ensure consistent filtration behavior across large fabric batches.
By contrast, application-specific requirements such as dust collection or liquid separation influence fabric density and surface finish. This is why filtration fabric producers often customize weaving parameters to match industrial usage scenarios.
Q2: How does fabric structure influence filtration performance?
Fabric structure directly affects filtration efficiency, airflow resistance, and service life. In an Industrial Filtration Fabric, weave pattern selection plays a major role in balancing permeability and particle retention. Tighter weaves improve capture rates, while more open constructions allow for reduced pressure drop.
A Multifilament Filter Textile benefits from its multi-strand construction, which creates micro-channels between filaments. These channels enhance particle interception without significantly restricting airflow. During production, loom settings must be carefully adjusted to maintain structural consistency throughout the fabric roll.
For applications that involve mechanical attachment, structural integrity becomes even more important. This is where reinforcement zones and edge treatments are introduced during the manufacturing process.
Q3: Why are sewing processes critical for filter bag production?
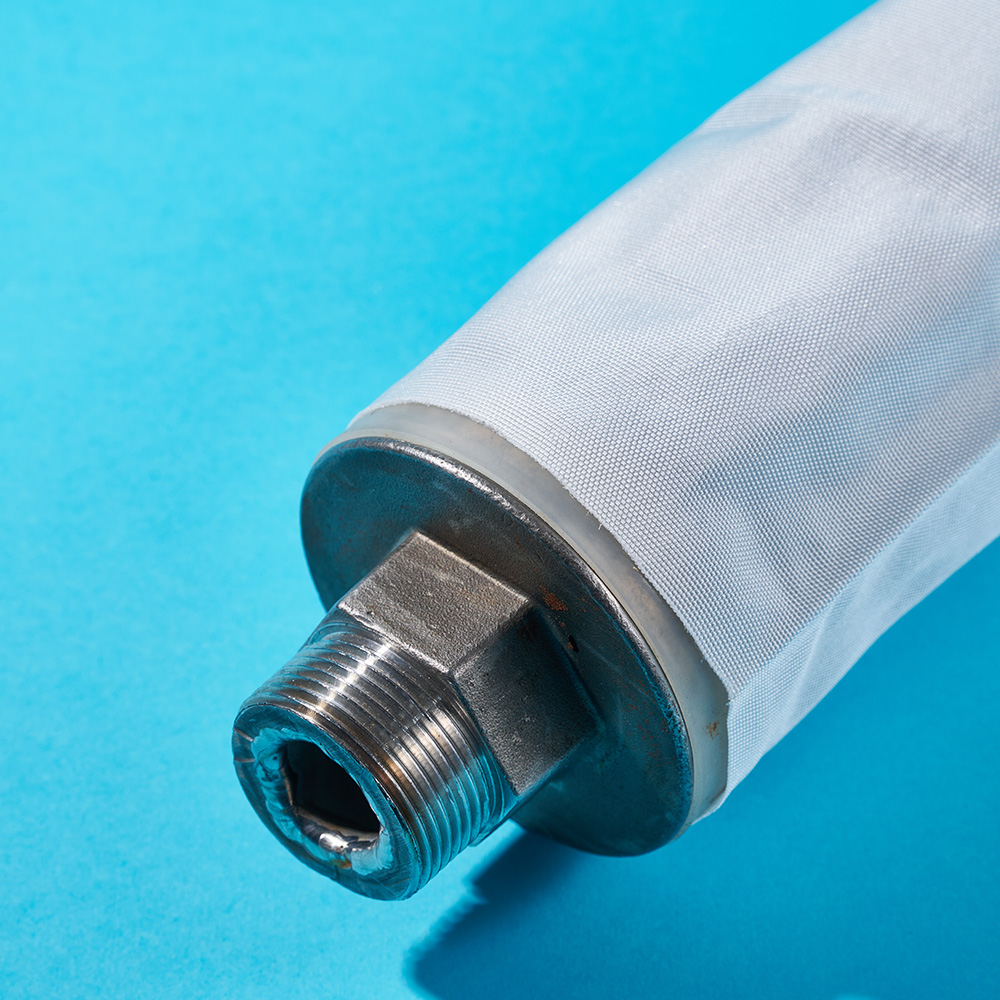
A Sewing Unit Filter Bag is not simply cut from filtration fabric and assembled. The sewing process itself can influence both filtration efficiency and bag lifespan. Needle selection, stitch density, and seam placement must be aligned with the characteristics of the base fabric.
When working with an Industrial Filtration Fabric, manufacturers typically reinforce stress points around seams to reduce the risk of tearing under operational load. Improper sewing can create leakage paths, reducing overall filtration effectiveness.
For fabrics made from Multifilament Filter Textile, sewing tension requires careful control. Excessive tension may damage filaments, while insufficient tension can lead to loose seams. As a result, many filter bag producers rely on specialized sewing units designed specifically for filtration textiles.
Q4: How do manufacturers align fabric types with application requirements?
Different industrial sectors demand different filtration outcomes. Cement plants, chemical processing facilities, and food-grade operations all require tailored solutions. The table below outlines general considerations used during product development:
| Application Condition |
Fabric Focus |
Manufacturing Consideration |
| High dust load |
Particle retention |
Weave density adjustment |
| Moist environments |
Moisture resistance |
Fiber treatment process |
| Continuous operation |
Durability |
Filament strength control |
A Sewing Unit Filter Bag designed for continuous-duty environments often incorporates reinforced seams and compatible thread materials. Meanwhile, selecting a Multifilament Filter Textile allows manufacturers to meet strength requirements without increasing fabric weight.
Q5: What quality control steps are involved in filtration textile manufacturing?
Quality control is integrated at every production stage. For an Industrial Filtration Fabric, inspections begin at raw fiber intake and continue through weaving, finishing, and final packaging. Parameters such as air permeability, tensile strength, and thickness uniformity are routinely tested.
During assembly, each Sewing Unit Filter Bag undergoes seam integrity checks to confirm stitching consistency. Any deviation can compromise performance during installation. For fabrics produced as Multifilament Filter Textile, filament cohesion and surface consistency are also examined to ensure stable filtration behavior.
By maintaining structured inspection protocols, manufacturers support predictable product performance across various industrial filtration systems.
From fiber selection to final assembly, filtration textile manufacturing requires coordinated control over materials, structure, and processing techniques. Whether producing an Industrial Filtration Fabric for large-scale systems or assembling a Sewing Unit Filter Bag for specific installations, attention to detail defines long-term usability. Through controlled production of Multifilament Filter Textile, manufacturers continue to support evolving industrial filtration demands with reliable, application-focused solutions.

 عربى
عربى