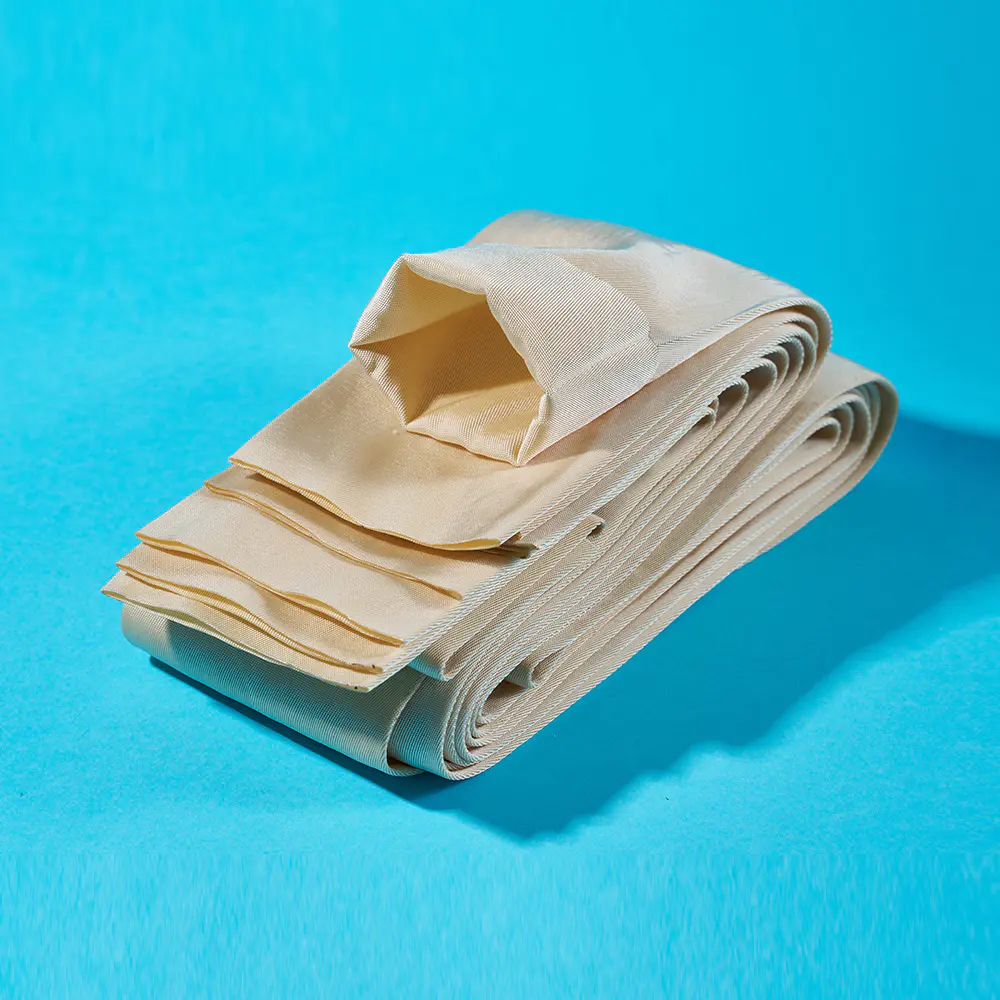
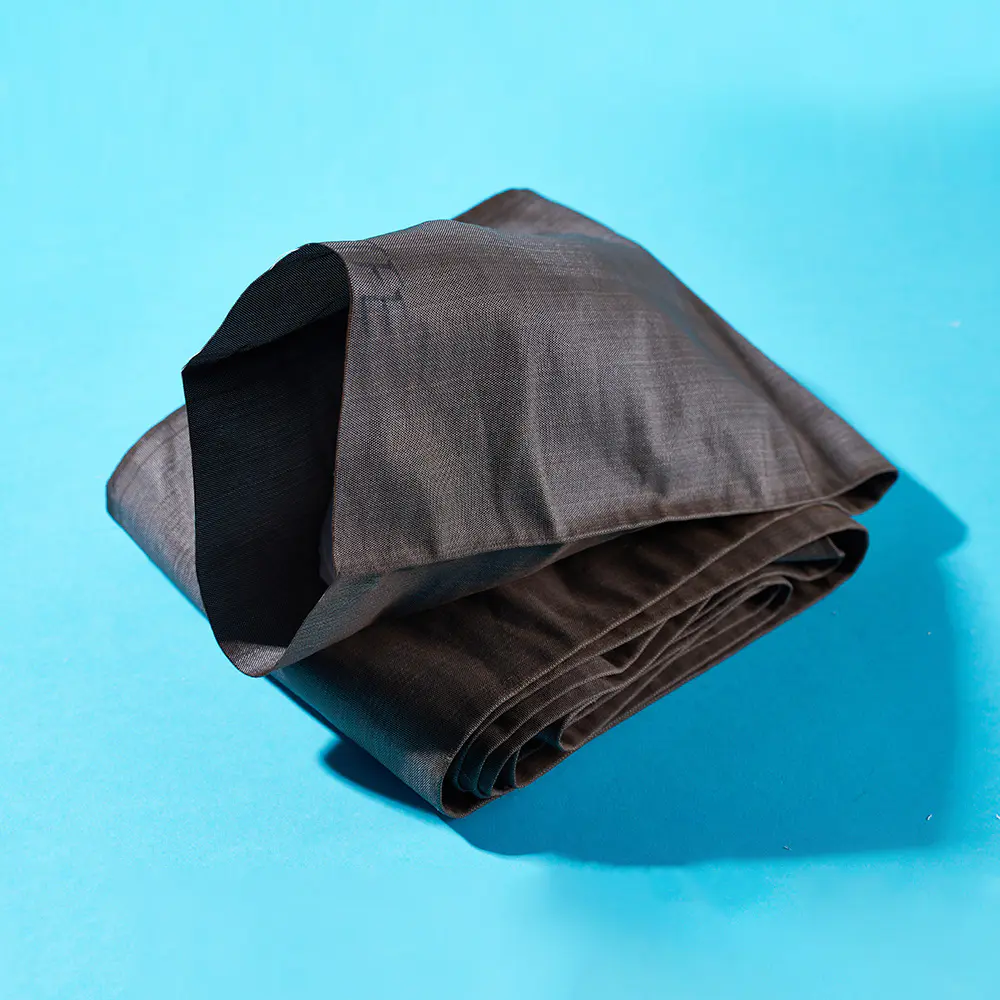
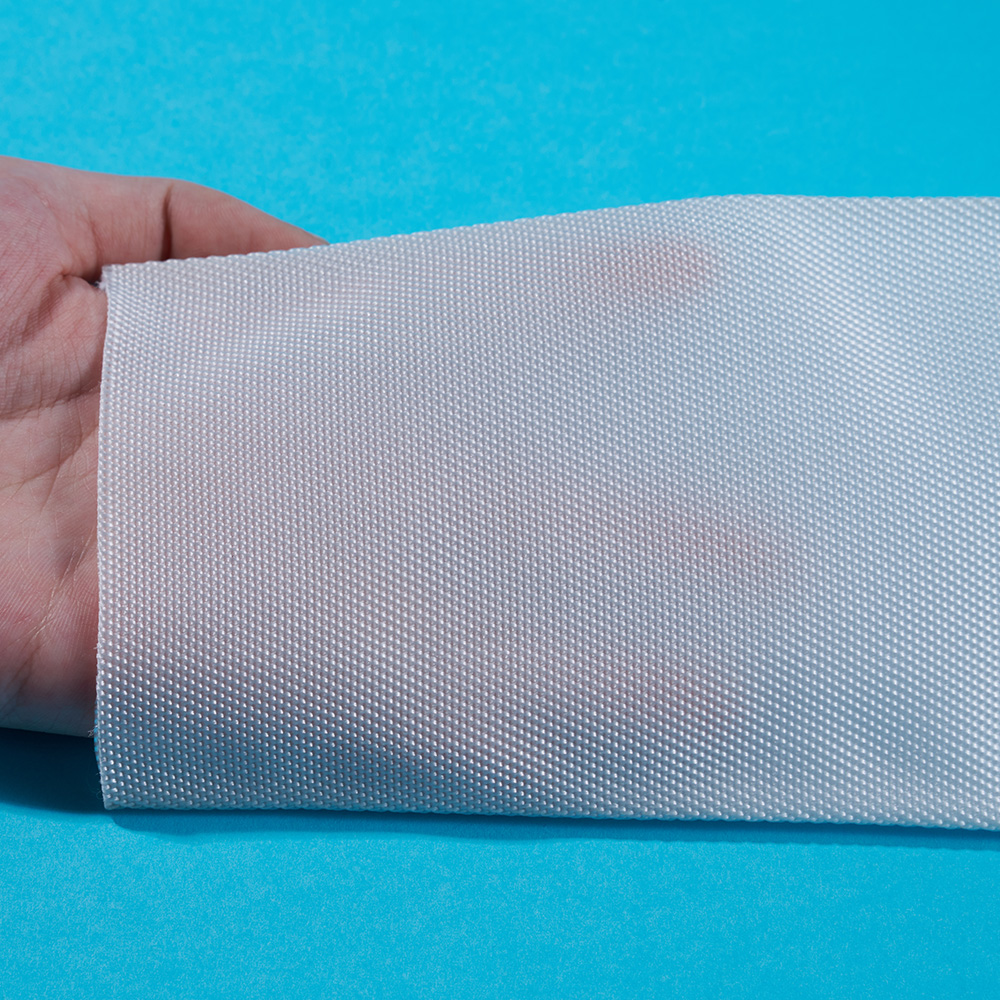
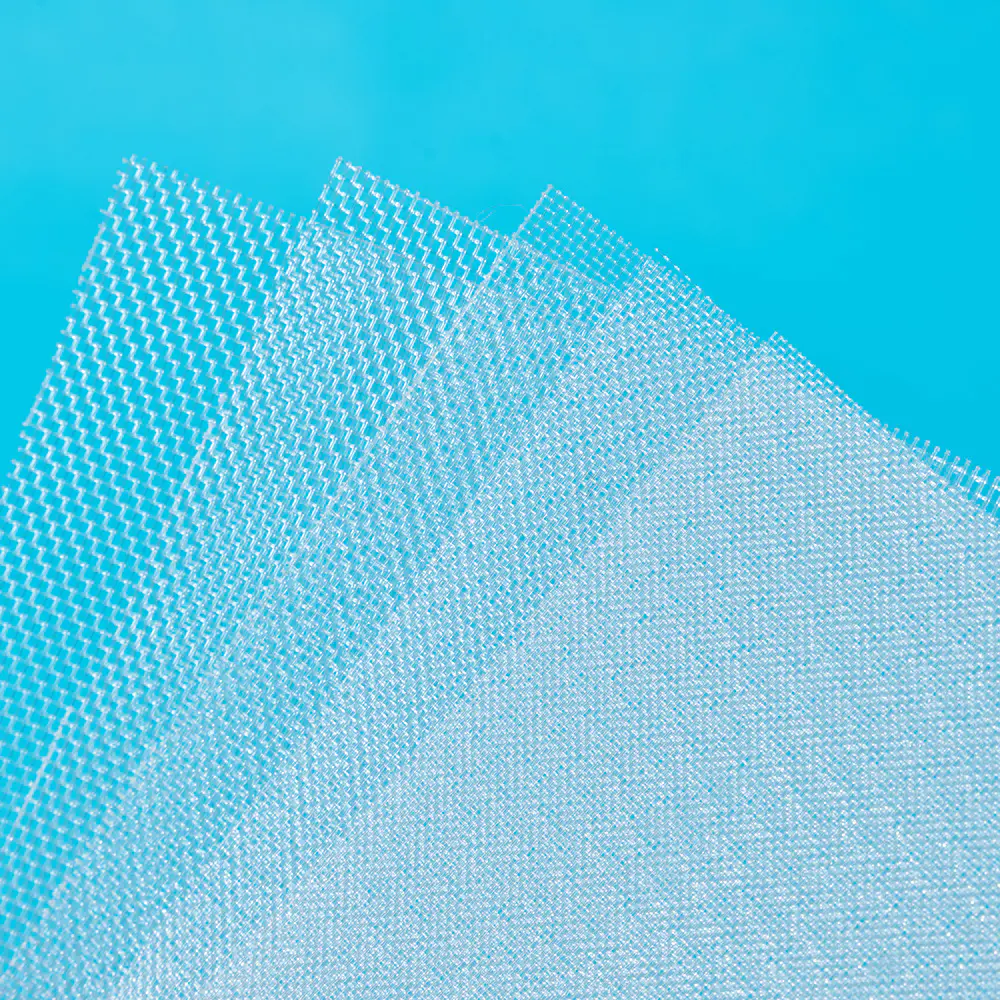
In recent years, the filtration sector has witnessed a quiet yet profound evolution, driven largely by advancements in material science and engineering. Among these developments, multifilament filter cloth has steadily risen to prominence, establishing itself as a cornerstone technology for a diverse array of industrial applications. Unlike its monofilament counterpart, which is woven from single, continuous strands, multifilament filter cloth is constructed from multiple fine filaments twisted or bundled together into a single yarn. This fundamental structural difference unlocks a unique combination of properties that is proving indispensable for modern separation processes.
The inherent advantage of multifilament filter cloth lies in its predominant performance profile. The dense network of fine filaments creates a smoother surface with a greater number of interstitial spaces, allowing for exceptionally fine particle retention. This makes it particularly effective in applications where clarity of the filtrate is paramount. Furthermore, the complex yarn structure offers outstanding stability and durability under pressure, resisting elongation and maintaining precise pore size distribution over extended operational cycles. This consistency is critical for ensuring predictable and reliable filtration outcomes, small product loss and process variability.
The material versatility of multifilament filter cloth further broadens its appeal. It can be manufactured from a wide range of synthetic polymers, including polypropylene, polyester, and nylon, each selected for its specific chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength. Polypropylene multifilament cloth, for instance, is widely favored for its outstanding resistance to acids and alkalis, making it a mainstay in chemical processing and mineral dewatering. Polyester variants, known for their robustness and resistance to abrasion, find heavy use in demanding sectors like ceramics and pigments. This adaptability allows engineers to specify a fabric superb tailored to the chemical and physical challenges of their specific process.
In practical application, multifilament filter cloth is demonstrating significant impact across key industries. In the environmental sector, it is crucial for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, where its fine filtration capabilities help meet stringent discharge regulations by efficiently removing suspended solids. The mining and metallurgy industries rely on it for dewatering concentrates and tailings, where its ability to handle abrasive slurries and produce dry cake is invaluable for resource recovery and waste management. Similarly, in food and beverage production, specific grades of multifilament cloth ensure hygienic separation, contributing to product purity and safety.
The operational benefits extend beyond mere separation efficiency. The robust nature of high-quality multifilament filter cloth contributes to longer service life and reduced downtime. When maintenance is required, many modern weaves are designed for easier cake release and cleaning, enhancing overall operational productivity. These factors collectively contribute to a lower total cost of ownership, making it an economically sound investment despite potentially higher initial costs compared to some alternatives.
Innovation in multifilament filter cloth technology continues. Developments are focused on enhancing surface treatments to further improve cake release properties, integrating composite materials for specialized applications, and refining weaving patterns to optimize flow rates and durability simultaneously. As global industries face increasing pressure to improve efficiency, sustainability, and product quality, the role of advanced filtration media becomes ever more critical. Within this landscape, multifilament filter cloth stands out not merely as a component, but as a key enabler of cleaner processes, higher yields, and more responsible industrial operations, solidifying its status as an essential material for the future of filtration.

 عربى
عربى