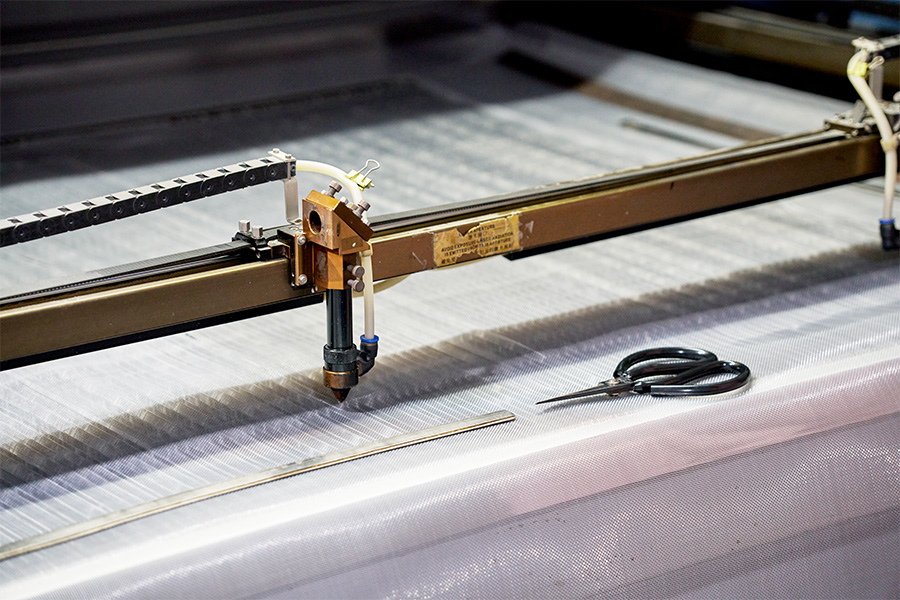
In the filtration industry, efficiency, precision, and durability are critical. Ultrasonic technologies have become a common solution for manufacturers aiming to improve the quality of their products. Specifically, Ultrasonic Welding for Filter Belts and Ultrasonic Cutting for Filter Sheets are applied to create reliable seams and precise shapes without damaging materials. Understanding the processes, applications, and benefits of these methods is essential for companies producing industrial and commercial filtration components.
What Is Ultrasonic Processing in Filtration?
Ultrasonic processing uses high-frequency vibrations, typically between 20 kHz and 40 kHz, to transfer energy into a material. This energy can either bond layers together or slice materials cleanly. Unlike traditional mechanical methods, ultrasonic techniques minimize stress and reduce the risk of fraying or material distortion.
| Feature | Ultrasonic Welding | Ultrasonic Cutting |
| Purpose | Bond filter belts | Cut filter sheets |
| Edge Quality | Smooth, sealed | Clean, precise |
| Material Stress | Low | Low |
| Speed | Fast | Fast |
| Materials | Thermoplastics, composites | Thermoplastics, composites |
By using ultrasonic methods, manufacturers can produce consistent, durable results for both filter belts and sheets, improving product performance in demanding applications.
How Does Ultrasonic Welding Work for Filter Belts?
Ultrasonic Welding for Filter Belts involves applying vibrations under pressure to layers of belt material. The vibrations generate localized heat that melts and bonds the material without adhesives or mechanical fasteners. This process creates a seamless joint that maintains flexibility and strength, even under repetitive stress.
Benefits
- Durable Seams: Welded joints endure repeated cycles of tension and stress, making them suitable for continuous operation.
- Clean Process: No glue or foreign materials are introduced, ensuring chemical safety in applications like food, water, or pharmaceutical filtration.
- Efficient Production: Welding is nearly instantaneous, enabling higher throughput without compromising quality.
- Design Flexibility: Complex seam patterns or belt geometries can be welded without deformation.
Industries such as wastewater treatment, beverage processing, and chemical filtration rely on welded belts to maintain consistent performance and reduce maintenance needs.
Why Choose Ultrasonic Cutting for Filter Sheets?
Ultrasonic Cutting for Filter Sheets uses similar high-frequency vibrations but focuses on slicing materials rather than bonding them. This process is ideal for producing sheets with precise dimensions and smooth edges. Traditional cutting methods often leave frayed edges or uneven shapes, which can reduce filter efficiency and performance.
Advantages
- Precise Edges: Cuts are consistent, which is critical when sheets must fit tight frames or housings.
- Reduced Waste: Accurate cutting minimizes offcuts, lowering material costs.
- Minimal Heat Impact: Ultrasonic cutting generates very little heat, preserving delicate fibers and preventing material distortion.
- Automation Ready: Cutting can be integrated into continuous production lines for high-volume output.
Industries requiring high-precision filtration, such as pharmaceuticals, laboratories, and medical equipment, benefit significantly from ultrasonic sheet cutting.
Welding vs. Cutting: Understanding Their Roles
While both ultrasonic welding and cutting are essential, their applications differ. The following table illustrates their main distinctions:
| Application | Welding | Cutting |
| Material Joining | Yes | No |
| Shape Formation | No | Yes |
| Seam Strength | High | Not Applicable |
| Material Loss | Low | Very Low |
| Automation | Moderate | High |
Manufacturers often use both techniques together: welding creates continuous filter belts, while cutting produces sheets tailored for specific machinery or filter housings.
Key Considerations for Implementation
To implement ultrasonic welding for filter belts or ultrasonic cutting for filter sheets, several factors must be considered:
- Material Compatibility: Thermoplastics such as polyester, polypropylene, and PTFE blends respond well to ultrasonic energy. Multi-layer or natural fiber composites may require testing and parameter adjustments.
- Frequency and Amplitude: Proper vibration frequency and amplitude ensure effective welding or precise cutting.
- Pressure and Speed: Both need fine-tuning to achieve consistent seam strength in belts or edge quality in sheets.
- Equipment Maintenance: Regular inspection of sonotrodes, anvils, and horns is essential to maintain process reliability and quality.
Small adjustments in process parameters can significantly affect product durability and edge consistency, particularly in high-volume manufacturing.
How Are Ultrasonic Processes Applied in Real Industries?
Water Filtration
Filter belts used in water treatment plants must handle constant exposure to water and chemical cleaning agents. Ultrasonic Welding for Filter Belts ensures that seams remain intact, preventing leakage and maintaining filtration efficiency. Ultrasonic Cutting for Filter Sheets allows precise fitting into frames, reducing bypass and improving overall performance.
Industrial Air Filtration
Air filtration systems, such as HVAC units and industrial purifiers, require sheets with exact dimensions. Ultrasonic cutting produces uniform edges, improving airflow efficiency and particle capture. Welded belts are also used in specialized conveyor systems for dust or particle collection.
Food and Beverage Industry
Hygiene is crucial in food processing. Welded belts provide a chemical-free bonding method, avoiding contamination risks while maintaining mechanical strength. Sheets cut ultrasonically fit perfectly into filtration housings, ensuring smooth operation and compliance with industry standards.
Material Responses and Process Optimization
The behavior of filter materials under ultrasonic energy varies. Polyester and polypropylene melt evenly under ultrasonic welding, producing strong, flexible seams. PTFE and composite layers may require slightly higher vibration amplitude or slower cutting speed to achieve consistent results.
Manufacturers often conduct trial runs to determine the optimal parameters for new materials. Small adjustments in welding pressure, cutting speed, or sonotrode design can significantly impact seam durability and sheet edge quality.
Maintenance and Longevity of Ultrasonic Equipment
Equipment maintenance is crucial for long-term process reliability. Sonotrodes, anvils, and horns wear over time, affecting vibration transmission and seam or cut quality. Regular cleaning prevents material buildup, while periodic recalibration of parameters ensures consistent welding and cutting performance. Proper maintenance prolongs equipment life and maintains product quality.
Supporting Customization and Flexibility
Custom filter designs are common in modern manufacturing. Ultrasonic cutting can produce intricate sheet shapes for laboratory filters, medical devices, or specialized industrial applications. Similarly, welding can create belts with unique seam patterns for modular assembly or specific mechanical requirements. The flexibility of ultrasonic processes allows manufacturers to respond quickly to evolving client needs without compromising quality.
Integration with Automation
Automation enhances the efficiency of ultrasonic processes. Both welding and cutting operations can be controlled by sensors and programmable logic controllers (PLCs), monitoring parameters such as pressure, speed, and amplitude in real-time. Automated systems ensure consistent quality, reduce labor requirements, and allow high-volume production.
Future Trends in Ultrasonic Filtration Technology
Emerging trends indicate further growth in ultrasonic applications for filter belts and sheets:
- AI-Assisted Quality Control: Sensors and machine learning can detect inconsistencies during welding or cutting, reducing defect rates.
- Energy Efficiency: New ultrasonic generators consume less power while maintaining output.
- Advanced Materials: Composite and multi-layered materials require adaptive ultrasonic processes, creating opportunities for specialized designs.
- Enhanced Tooling: Custom sonotrode shapes allow for more complex welds and cuts, supporting innovative filter configurations.
These advancements suggest that ultrasonic technology will continue to play a central role in filtration manufacturing.
Ultrasonic Welding for Filter Belts and Ultrasonic Cutting for Filter Sheets provide practical, reliable solutions for modern filtration needs. Welding ensures strong, seamless belts capable of repeated use, while cutting delivers precision sheets that fit tight tolerances. Together, these technologies enhance manufacturing efficiency, reduce material waste, and maintain consistent product quality.
Whether producing belts for industrial water treatment or sheets for medical filtration, ultrasonic processes offer the flexibility, precision, and durability required in demanding applications. Companies that implement these methods thoughtfully, considering material properties, process optimization, and automation integration, can achieve better performance, lower costs, and more adaptable production systems.

 عربى
عربى