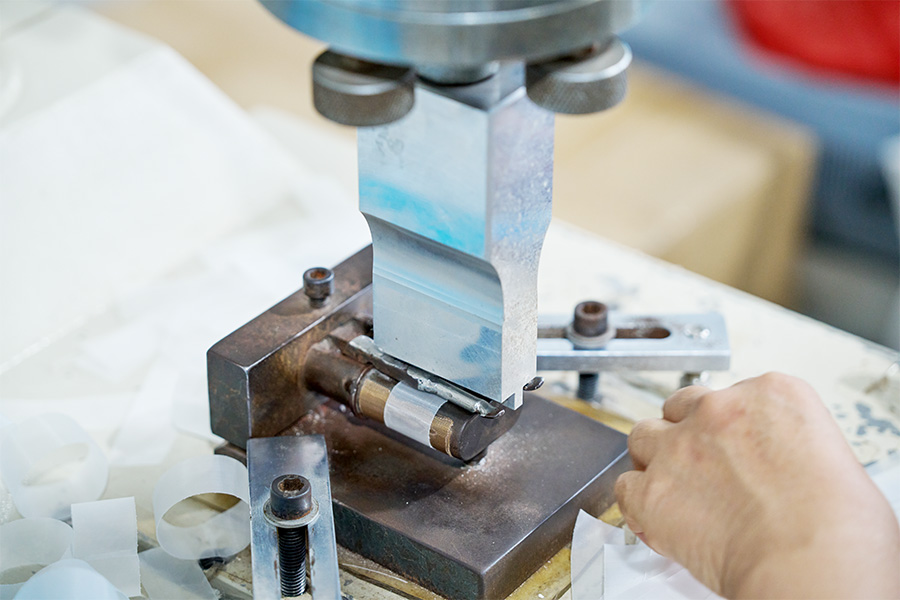
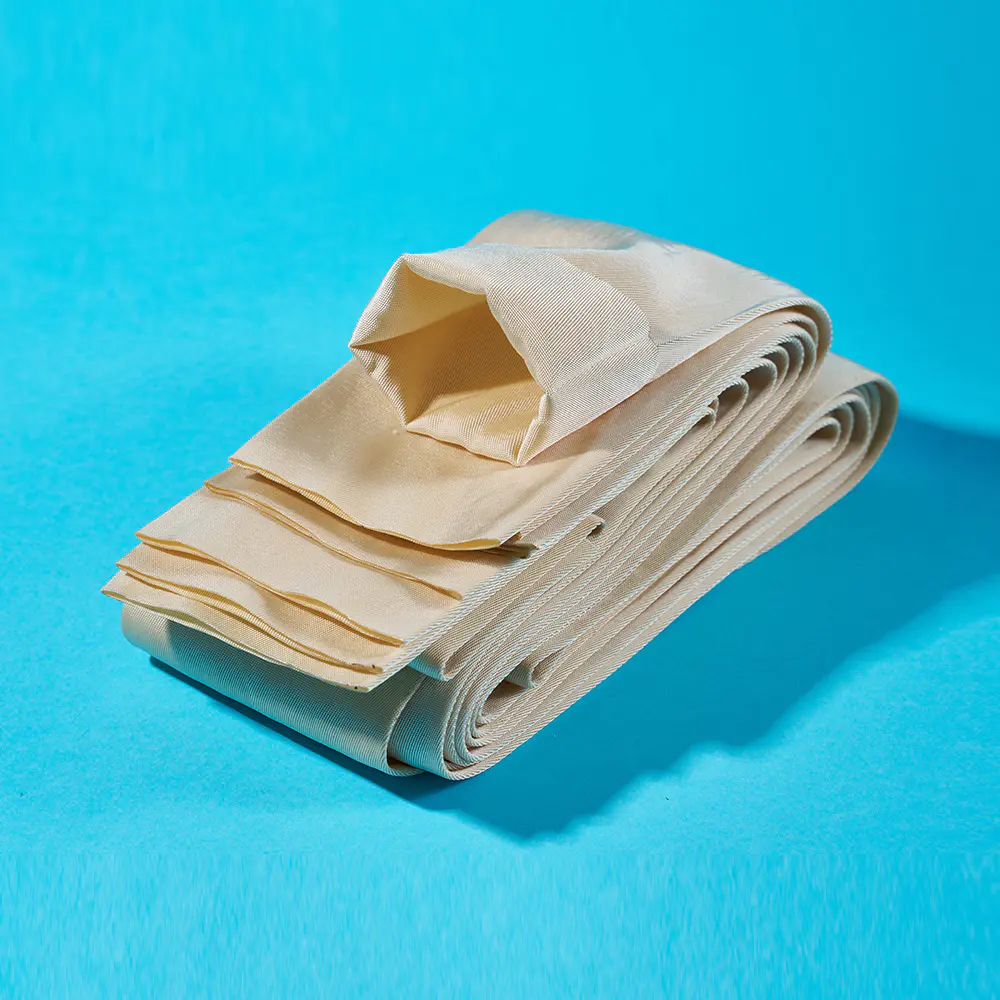
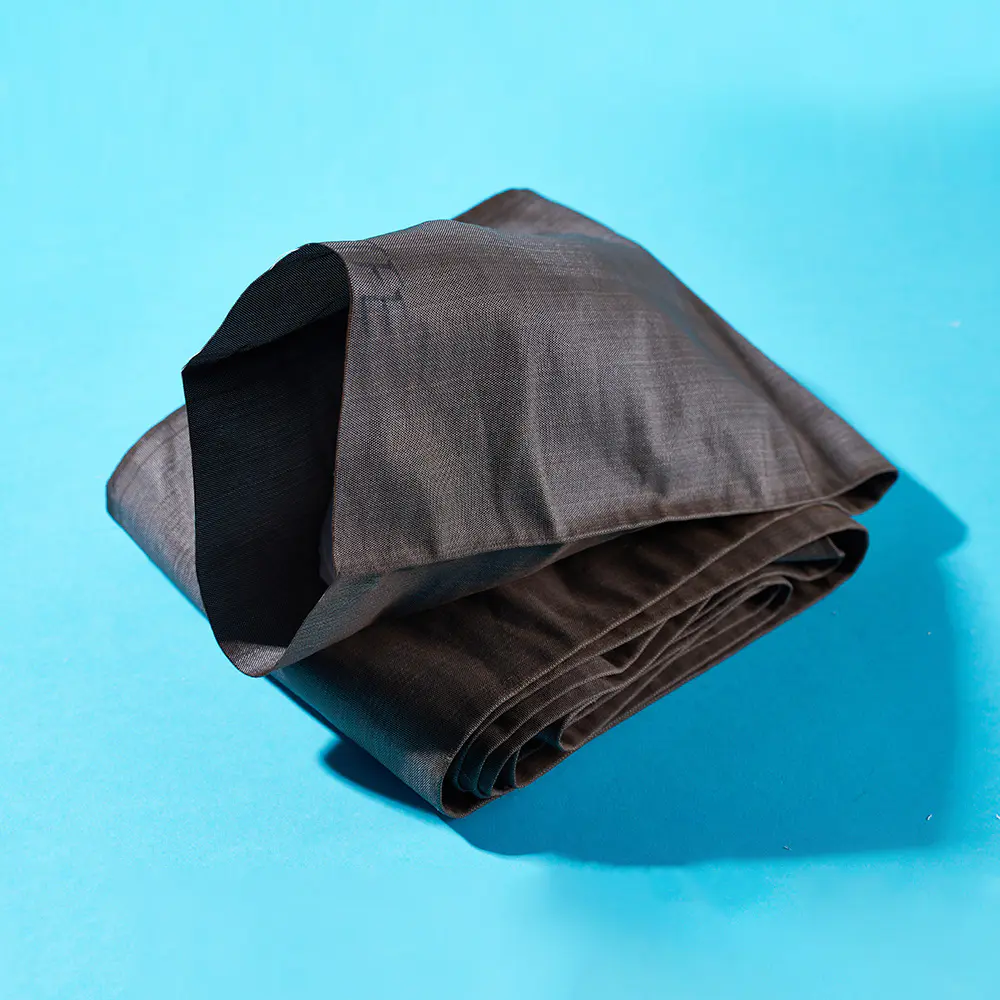
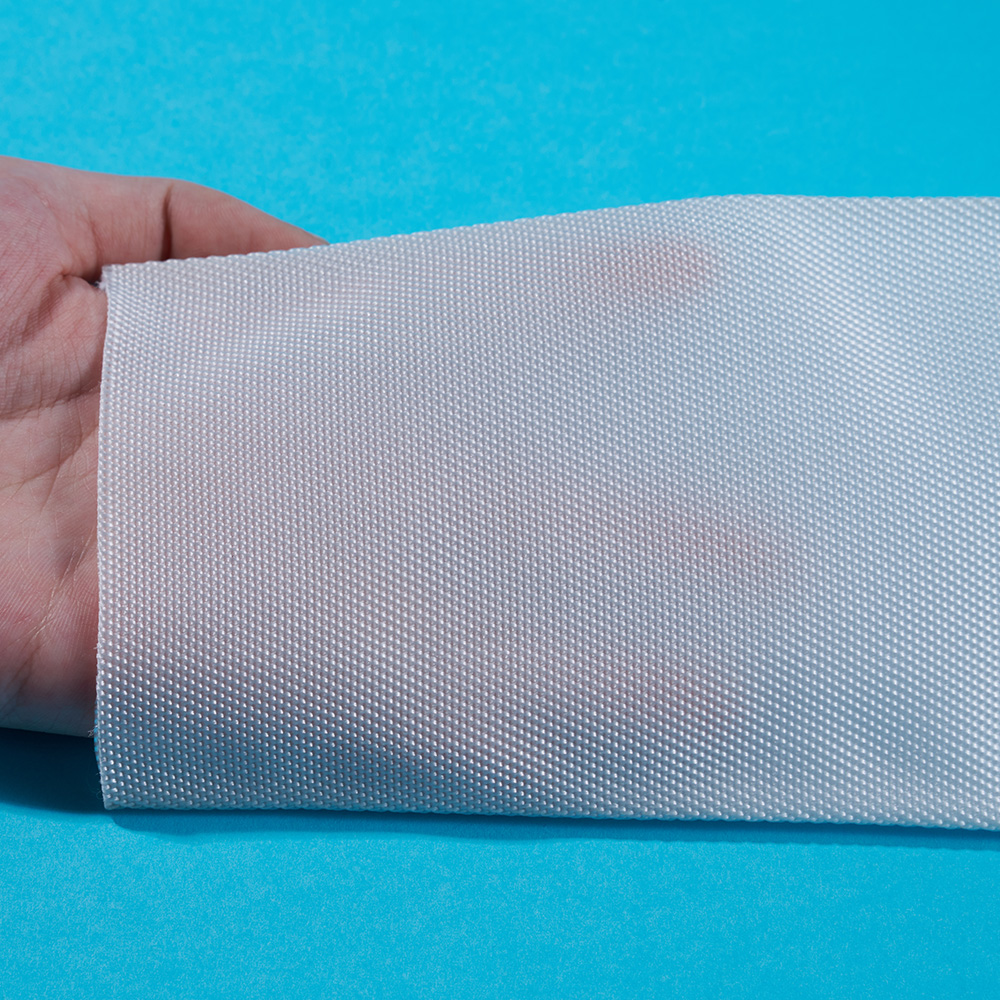
In modern industrial operations, filtration plays a critical role in ensuring clean air, liquids, and fuels. The choice of Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium can greatly affect system performance, maintenance costs, and operational safety. Companies producing filters rely on different types of media to meet the specific demands of applications, ranging from industrial machinery to automotive engines. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each type is essential for designing effective filtration systems.
What Is Filter Medium and Why Is It Important?
A filter medium is the core material responsible for removing contaminants from liquids, gases, or fuels. It acts as a barrier, capturing particles while allowing the fluid or air to pass through. Selecting the right medium can improve equipment lifespan, maintain efficiency, and reduce downtime.
Different applications require different media characteristics. For instance, Industrial Filter Medium is often designed for heavy-duty operations with high flow rates, while High Efficiency Filter Medium targets finer particles in sensitive systems. Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium is a broad category that addresses the diverse needs of air, water, and fuel filtration.
How Does Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium Work?
Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium serves to trap contaminants such as dust, dirt, rust, or microbial matter. Its effectiveness depends on factors like pore size, material composition, and layer thickness.
- Liquid filtration: Captures suspended particles and protects pumps, engines, and hydraulic systems.
- Gas filtration: Removes airborne particles that could damage sensitive equipment or compromise air quality.
- Fuel filtration: Ensures clean fuel delivery, preventing engine wear or injector clogging.
The performance of the medium is measured by efficiency ratings, pressure drop, and dirt-holding capacity. A well-designed filter medium can balance high efficiency with minimal flow resistance.
Why Choose Industrial Filter Medium?
Industrial Filter Medium is tailored for robust applications such as manufacturing plants, chemical processing, and large-scale HVAC systems. It is designed to handle high flow volumes and extended operational periods without significant pressure drop.
Advantages
- Durability: Able to withstand mechanical stress and prolonged exposure to fluids or gases.
- Adaptability: Can be customized for specific contaminants or operating conditions.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces maintenance frequency and replacement costs over time.
- Versatility: Suitable for oil, water, air, and gas filtration systems.
Industrial filter media often utilize synthetic fibers, cellulose blends, or metal mesh, depending on the filtration requirements. These materials ensure reliability in environments with varying temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposures.
How Does High Efficiency Filter Medium Differ?
High Efficiency Filter Medium focuses on capturing finer particles that standard industrial media may not retain. It is commonly used in environments where contamination control is critical, such as laboratories, pharmaceutical production, clean rooms, and precision manufacturing.
Key features of high-efficiency media include:
- Fine pore structure: Captures small dust, microbes, or submicron particles.
- Low pressure drop: Maintains airflow or fluid movement without straining equipment.
- Consistent performance: Retains filtering capacity over extended periods, even in high-load conditions.
- Chemical and thermal resistance: Suitable for processes involving solvents, oils, or hot gases.
By incorporating high-efficiency media, operators can improve overall system cleanliness and protect sensitive components from damage or contamination.
Comparing Filter Media Types
The following table highlights differences between common filter media types:
| Feature | Industrial Filter Medium | High Efficiency Filter Medium | Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium |
| Particle Retention | Moderate | Fine | Varies by application |
| Durability | High | Medium | High |
| Pressure Drop | Moderate | Low | Depends on flow |
| Applications | Factories, plants | Clean rooms, labs | Automotive, HVAC, fuel systems |
| Material Types | Synthetic fibers, cellulose, metal mesh | Microfiber, pleated media | Blend of synthetic and natural fibers |
Understanding these differences helps engineers and operators select the right medium for their specific needs.
How to Select the Right Filter Medium?
Choosing the appropriate medium involves assessing application requirements, operational conditions, and maintenance expectations.
- Contaminant Type and Size: Identify particles, microbes, or chemicals that need removal. High-efficiency media are preferable for submicron particles, while industrial media handle coarser debris.
- Flow Rate and Pressure: Ensure the medium allows adequate flow without excessive pressure drop.
- Chemical Compatibility: Consider exposure to oils, solvents, or corrosive substances.
- Temperature Range: Select a medium that can withstand operational temperatures without degrading.
- Maintenance Cycle: Evaluate dirt-holding capacity and replacement frequency to optimize operational cost.
By carefully evaluating these factors, companies can ensure consistent system performance and reduce the risk of equipment damage.
Applications of Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium
Automotive and Fuel Systems
Fuel systems require Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium to remove impurities that could clog injectors or damage engines. High-quality media ensure longer engine life and stable performance, even under high pressure and temperature fluctuations.
Industrial Manufacturing
Factories rely on Industrial Filter Medium to protect machinery and maintain air and water quality. Proper filtration prevents dust accumulation, reduces corrosion, and ensures that sensitive processes run smoothly.
Healthcare and Laboratories
In pharmaceutical labs and hospitals, High Efficiency Filter Medium removes tiny particles and microbial contaminants. These media maintain sterility, improve product quality, and meet strict regulatory standards.
HVAC and Environmental Control
HVAC systems in office buildings or industrial facilities benefit from a combination of industrial and high-efficiency media. Industrial media handle dust and large particles, while high-efficiency media capture finer particles, improving indoor air quality.
Material Considerations for Filter Media
The choice of material directly affects the performance of the filter medium:
- Cellulose-based media: Affordable, widely used in liquid filtration.
- Synthetic fibers: Durable, resistant to chemical exposure, suitable for industrial applications.
- Microfiber or nanofiber layers: Used in high-efficiency applications for capturing submicron particles.
- Metal meshes: Provide structural support and are reusable in some industrial systems.
Selecting the right material ensures that the medium performs effectively without clogging, breaking down, or losing efficiency over time.
Maintenance and Longevity
Proper maintenance extends the life of filter media and improves system reliability. Key steps include:
- Regular inspection: Check for clogging, tears, or chemical damage.
- Scheduled replacement: Follow manufacturer recommendations to avoid performance loss.
- Cleaning procedures: Some industrial or metal media can be cleaned and reused, while synthetic or high-efficiency media may require complete replacement.
Maintenance planning is essential to avoid unexpected downtime and maintain consistent filtration quality.
Future Trends in Filter Media
Advancements in filter media technology continue to improve efficiency and adaptability:
- Nanofiber media: Enhance high-efficiency performance without increasing pressure drop.
- Hybrid media: Combine multiple layers or materials to capture a wider range of contaminants.
- Sustainable materials: Develop biodegradable or recyclable media to reduce environmental impact.
- Smart filters: Sensors integrated with filters can monitor flow, pressure drop, and contamination levels in real time.
These innovations allow filtration systems to adapt to stricter environmental regulations, higher operational demands, and more sensitive applications.
Choosing the right filter medium is critical for reliable filtration performance. Liquid/Gas/Fuel Filter Medium ensures clean fuels, air, and liquids for safe and efficient operation. Industrial Filter Medium supports robust, high-flow applications, while High Efficiency Filter Medium captures fine particles for sensitive environments.
By understanding material properties, application requirements, and operational conditions, engineers and operators can select media that improve system longevity, reduce maintenance costs, and maintain efficiency. Incorporating proper maintenance and considering emerging technologies further enhances performance, ensuring that filtration systems meet the demands of modern industry.

 عربى
عربى